If you’ve heard the term “Valvular heart disease ICD 10,” you might be wondering about the connection between this medical code and conditions like congestive heart failure and heart disease. In this comprehensive article, we’ll delve into the world of heart health, discussing what heart failure is, its causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, treatment options, and ways to prevent further deterioration. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of valvular heart disease, its association with heart failure, and how to manage your heart health effectively.
What Is Heart Failure?
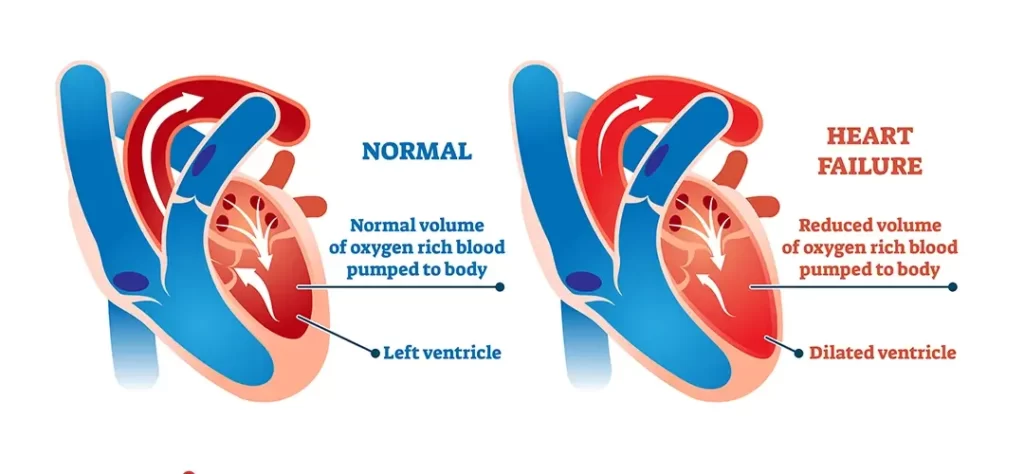
Heart failure is a serious medical condition where the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively is compromised. This can result in inadequate blood circulation throughout the body, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. It’s essential to note that heart failure doesn’t mean the heart has stopped working; rather, it’s struggling to pump blood efficiently.
What Causes Heart Failure?
Several factors can contribute to the development of heart failure, including:
- Coronary Artery Disease: Blocked or narrowed arteries can reduce blood flow to the heart muscle, weakening it over time.
- High Blood Pressure: Prolonged high blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, eventually leading to heart muscle weakening.
- Valvular Heart Disease: Conditions affecting the heart valves, like stenosis or regurgitation, can strain the heart and lead to heart failure.
- Cardiomyopathy: Damage to the heart muscle, often due to infections, alcohol abuse, or genetics, can impair the heart’s pumping ability.
Heart Failure Symptoms
Heart failure presents various symptoms, including:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in legs, ankles, or abdomen
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Persistent cough or wheezing
What Are the Types of Heart Failure?
Heart failure is categorized into two main types:
- Systolic Heart Failure: The heart’s left ventricle struggles to contract effectively, reducing the heart’s pumping capacity.
- Diastolic Heart Failure: The heart’s left ventricle has difficulty relaxing, limiting its ability to fill with blood properly.
How Is Heart Failure Diagnosed?
Medical professionals diagnose heart failure using a combination of medical history, physical examinations, imaging tests (such as echocardiograms), and diagnostic criteria outlined in the ICD-10.
Heart Failure Treatment
The treatment approach varies based on the type and severity of heart failure. It may include:
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, smoking cessation)
- Medications to control symptoms and improve heart function
- Medical devices (pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators)
- Surgical interventions (heart valve repair or replacement)
- Heart transplant in severe cases
Stages of Heart Failure
Heart failure is categorized into four stages, helping medical professionals determine the appropriate treatment plan:
- Stage A: High risk for heart failure but without structural heart damage or symptoms.
- Stage B: Structural heart damage but without symptoms.
- Stage C: Structural damage with prior or current symptoms of heart failure.
- Stage D: Advanced heart failure requiring specialized interventions.
How Can I Prevent Heart Failure From Getting Worse?
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing heart failure progression:
- Adhering to prescribed medications
- Monitoring fluid intake and weight
- Following a heart-healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress and getting adequate sleep
How Can I Prevent Further Heart Damage?
To prevent further damage, it’s essential to manage underlying conditions contributing to heart failure:
- Controlling blood pressure
- Managing diabetes
- Treating coronary artery disease
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
What Medications Should I Avoid if I Have Heart Failure?
Certain medications can worsen heart failure symptoms. Consult your doctor before taking:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Some diabetes medications
- Certain antidepressants
How Can I Improve My Quality of Life With Heart Failure?
You can enhance your quality of life by:
- Following your treatment plan diligently
- Engaging in physical activity as advised
- Seeking emotional support from loved ones
- Participating in cardiac rehabilitation programs
Can Surgery Be Used to Treat Heart Failure?
Surgery may be necessary in advanced cases:
- Heart Valve Repair/Replacement: To address valvular heart disease contributing to heart failure.
- Coronary Bypass Surgery: To improve blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Heart Transplant: In severe cases of heart failure.
Heart Failure Treatment Is a Team Effort
Managing heart failure involves collaboration between patients, healthcare providers, and specialists. Regular check-ups and communication are essential to adjust treatment plans as needed.
When Should I Get Emergency Care?
Seek emergency medical attention if you experience severe symptoms like chest pain, difficulty breathing, or fainting. These could indicate a heart attack or a life-threatening heart rhythm.
What Is the Outlook for People With Heart Failure?
The outlook varies depending on the severity of heart failure, underlying health conditions, and adherence to treatment. With proper management and lifestyle changes, many people can lead fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis.
In conclusion, understanding valvular heart disease ICD 10 and its relationship with congestive heart failure and heart disease is crucial for maintaining optimal heart health. By following medical advice, making lifestyle adjustments, and seeking timely care, you can significantly improve your quality of life and outlook.
FAQs
What is valvular heart disease ICD 10?
Valvular heart disease ICD 10 is a medical code used to classify and diagnose heart conditions, specifically those related to heart valve problems.
Can heart failure be prevented entirely?
While not always preventable, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing underlying health issues can significantly reduce the risk of heart failure.
Are there any warning signs of heart failure worsening?
Yes, warning signs include increased shortness of breath, sudden weight gain, and persistent swelling.
Can heart failure occur suddenly?
Heart failure usually develops gradually over time due to underlying health conditions. However, certain situations, like a heart attack, can lead to sudden heart failure.
Is heart failure reversible?
While heart damage is generally irreversible, timely and effective treatment can manage symptoms, slow progression, and improve quality of life.