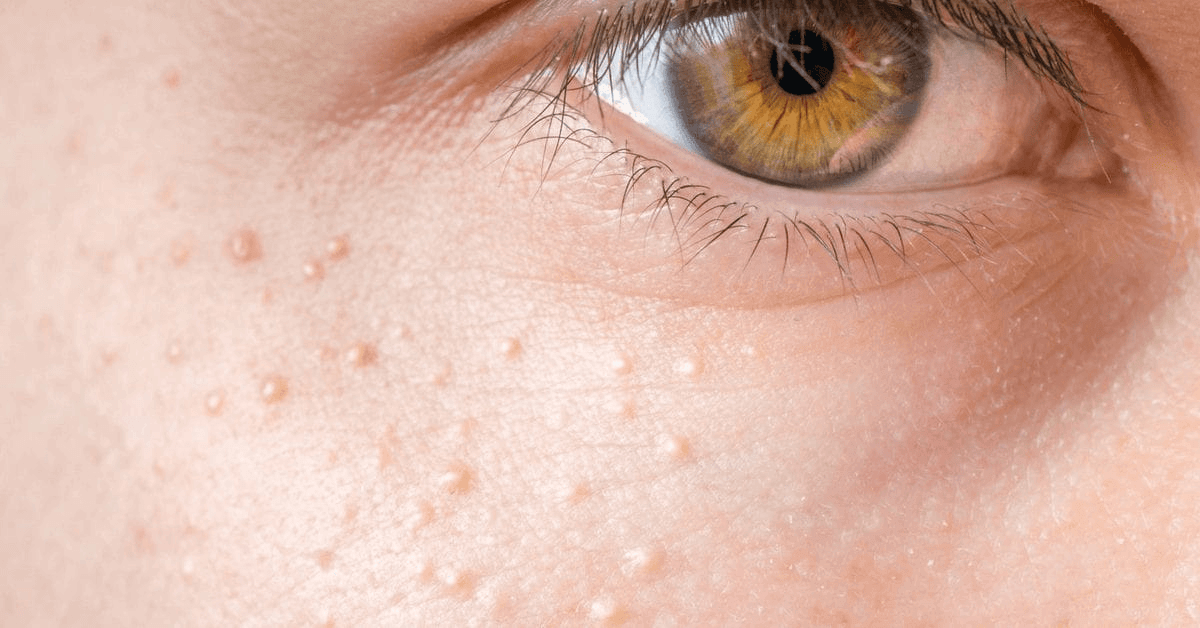
Milialar, often referred to as Milia, are small, keratin-filled cysts that appear beneath the skin’s surface. These tiny, pearly white bumps are a common dermatological concern for many individuals. Understanding their origins, types, and treatment methods is crucial for effectively managing and preventing their occurrence.
What Causes Milia?
Primary Milia
- Congenital Milia: These tiny cysts can be present at birth, resulting from the retention of skin cells.
- Benign Primary Milia: Occurring in children and adults, these milia develop due to the sweat glands’ inability to properly exfoliate skin cells.
- Milia En Plaque (MEP): A rare form characterized by clusters of milia on raised, reddened patches of skin.
- Multiple Eruptive Milia: Manifesting in numerous tiny bumps erupting in groups across the face or upper body.
- Genodermatosis-associated: Some genetic skin disorders can lead to the development of milia.
Secondary Milia
- Disease-associated: Certain skin conditions like blistering disorders or bullous pemphigoid may prompt secondary milia formation.
- Medication-associated: Long-term use of certain topical medications can trigger milia.
- Trauma-associated: Skin injuries or burns can cause milia as part of the healing process.
How to Get Rid of Milia
Extraction
Dermatologists perform extraction by delicately piercing the Milialar with a sterile needle to remove the trapped keratin.
Chemical Peels
- Glycolic Acid: This alpha hydroxy acid effectively exfoliates the skin, aiding in the removal of milia.
- Lactic Acid: Similarly, lactic acid helps in the gentle exfoliation and smoothing of the affected area.
- Salicylic Acid: Known for its deep exfoliation properties, it assists in preventing new milia formation.
Retinoids
Topical retinoids are effective in accelerating cell turnover, preventing blockages, and ultimately aiding in milia reduction.
Can You Remove Milia at Home?
While some home remedies like gentle exfoliation or steaming can help alleviate milia, self-removal is not recommended due to the risk of scarring or infection. It’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for safe and effective removal.
Prevention
- Regular Exfoliation: Using gentle exfoliants can prevent the buildup of dead skin cells, reducing the likelihood of milia formation.
- Avoid Harsh Products: Refrain from using overly thick or greasy skincare products that could clog pores and lead to milia.
- Sun Protection: Shielding the skin from excessive sun exposure can prevent damage that might result in milia.
Review
Understanding the different types, causes, and treatment options for Milialar is crucial in effectively managing this dermatological concern. While some remedies can aid in milia reduction, professional guidance is recommended for safe and optimal treatment.
FAQs
- Can Milia go away on their own?
- Congenital milia often vanish naturally, while others may require intervention.
- Congenital milia often vanish naturally, while others may require intervention.
- Are chemical peels safe for milia removal?
- When performed by a professional, chemical peels can be safe and effective.
- When performed by a professional, chemical peels can be safe and effective.
- Can squeezing milia at home be harmful?
- Squeezing or attempting to remove milia at home can lead to scarring or infection.
- Squeezing or attempting to remove milia at home can lead to scarring or infection.
- Can dietary changes help prevent milia?
- While a healthy diet benefits skin health, there’s no direct link between diet and milia prevention.
- While a healthy diet benefits skin health, there’s no direct link between diet and milia prevention.
- Is sunscreen important in preventing milia?
- Yes, sunscreen helps prevent skin damage, potentially reducing the risk of milia formation.